The CSS background properties are used to add background effects for elements.
In these chapters, you will learn about the following CSS background properties:
background-colorbackground-imagebackground-repeatbackground-attachmentbackground-positionbackground(shorthand property)
CSS background-color
The background-color property specifies the background color of an element.
Example
The background color of a page is set like this:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
body {
background-color: lightblue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
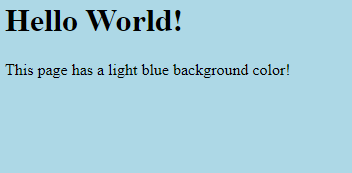
<h1>Hello World!</h1>
<p>This page has a light blue background color!</p>
</body>
</html>
Result:
With CSS, a color is most often specified by:
- a valid color name – like “red”
- a HEX value – like “#ff0000”
- an RGB value – like “rgb(255,0,0)”
Look at CSS Color Values for a complete list of possible color values.
Other Elements
You can set the background color for any HTML elements:
Example
Here, the <h1>, <p>, and <div> elements will have different background colors:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
h1 {
background-color: green;
}
div {
background-color: lightblue;
}
p {
background-color: yellow;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>CSS background-color example!</h1>
<div>
This is a text inside a div element.
<p>This paragraph has its own background color.</p>
We are still in the div element.
</div>
</body>
</html>
Result:

Opacity / Transparency
The opacity property specifies the opacity/transparency of an element. It can take a value from 0.0 – 1.0. The lower value, the more transparent:
Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
div {
background-color: green;
}
div.first {
opacity: 0.1;
}
div.second {
opacity: 0.3;
}
div.third {
opacity: 0.6;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Transparent Boxes</h1>
<p>When using the opacity property to add transparency to the background of an element, all of its child elements become transparent as well. This can make the text inside a fully transparent element hard to read:</p>
<div class="first">
<h1>opacity 0.1</h1>
</div>
<div class="second">
<h1>opacity 0.3</h1>
</div>
<div class="third">
<h1>opacity 0.6</h1>
</div>
<div>
<h1>opacity 1 (default)</h1>
</div>
</body>
</html>
Result:

CSS background-image
The background-image property specifies an image to use as the background of an element.
By default, the image is repeated so it covers the entire element.
Example
Set the background image for a page:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
body {
background-image: url("paper.gif");
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
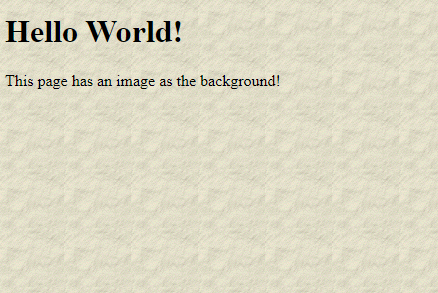
<h1>Hello World!</h1>
<p>This page has an image as the background!</p>
</body>
</html>
Result:
Example
This example shows a bad combination of text and background image. The text is hardly readable:
body {
background-image: url(“bgdesert.jpg”);
}
Result:

The background image can also be set for specific elements, like the <p> element:
Example
p {
background-image: url(“paper.gif”);
}
Result:

CSS background-repeat
By default, the background-image property repeats an image both horizontally and vertically.
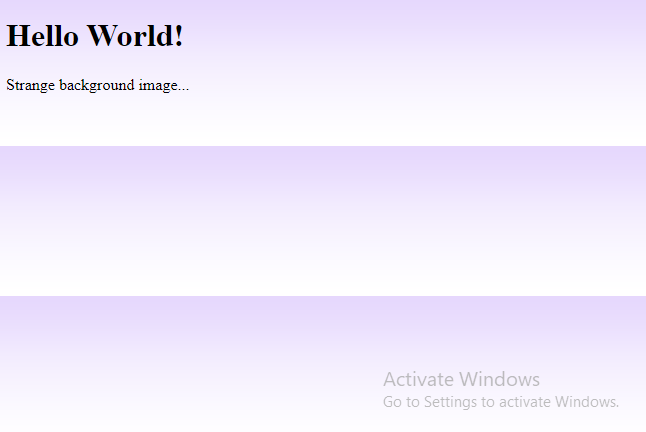
Some images should be repeated only horizontally or vertically, or they will look strange, like this:
Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
body {
background-image: url("gradient_bg.png");
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello World!</h1>
<p>Strange background image...</p>
</body>
</html>
Result:
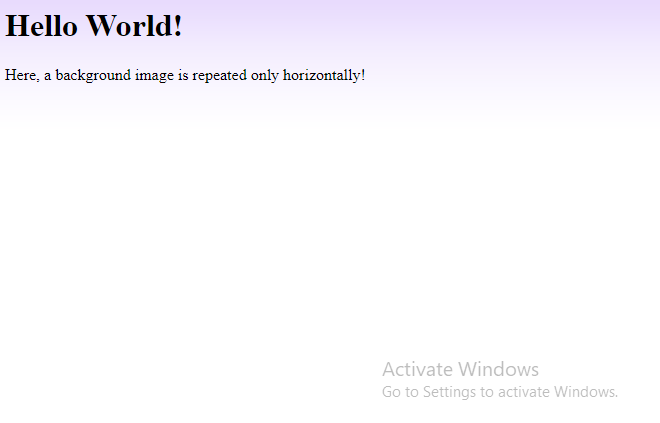
If the image above is repeated only horizontally (background-repeat: repeat-x;), the background will look better:
Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
body {
background-image: url("gradient_bg.png");
background-repeat: repeat-x;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello World!</h1>
<p>Here, a background image is repeated only horizontally!</p>
</body>
</html>
Result:
CSS background-repeat: no-repeat
Showing the background image only once is also specified by the background-repeat property:
Example
Show the background image only once:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
body {
background-image: url("img_tree.png");
background-repeat: no-repeat;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello World!</h1>
<p>W3Schools background image example.</p>
<p>The background image only shows once, but it is disturbing the reader!</p>
</body>
</html>
Result:
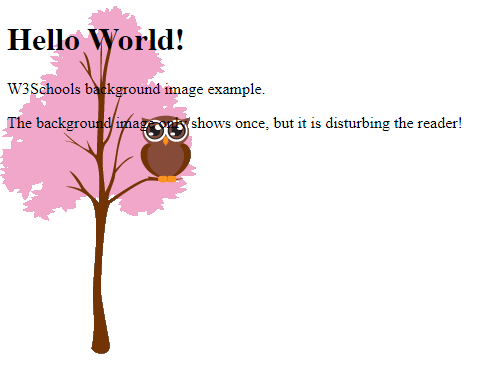
In the example above, the background image is placed in the same place as the text. We want to change the position of the image, so that it does not disturb the text too much.
CSS background-position
The background-position property is used to specify the position of the background image.
Example
Position the background image in the top-right corner:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
body {
background-image: url("img_tree.png");
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-position: right top;
margin-right: 200px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello World!</h1>
<p>Here, the background image is only shown once. In addition it is positioned away from the text.</p>
<p>In this example we have also added a margin on the right side, so that the background image will not disturb the text.</p>
</body>
</html>
Result:

CSS background-attachment
The background-attachment property specifies whether the background image should scroll or be fixed (will not scroll with the rest of the page):
Example
Specify that the background image should be fixed:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
body {
background-image: url("img_tree.png");
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-position: right top;
margin-right: 200px;
background-attachment: fixed;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
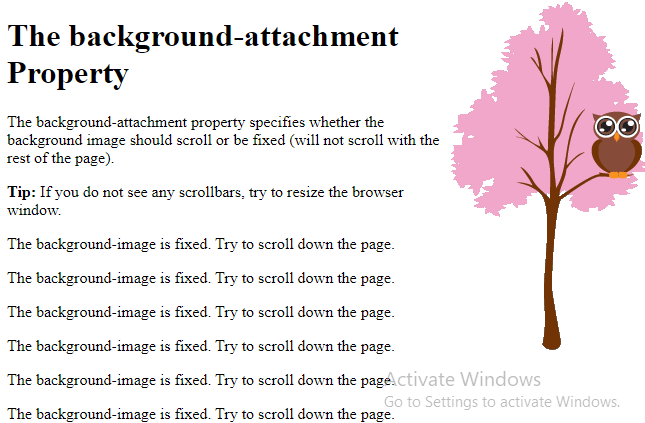
<h1>The background-attachment Property</h1>
<p>The background-attachment property specifies whether the background image should scroll or be fixed (will not scroll with the rest of the page).</p>
<p><strong>Tip:</strong> If you do not see any scrollbars, try to resize the browser window.</p>
<p>The background-image is fixed. Try to scroll down the page.</p>
<p>The background-image is fixed. Try to scroll down the page.</p>
<p>The background-image is fixed. Try to scroll down the page.</p>
<p>The background-image is fixed. Try to scroll down the page.</p>
<p>The background-image is fixed. Try to scroll down the page.</p>
<p>The background-image is fixed. Try to scroll down the page.</p>
<p>The background-image is fixed. Try to scroll down the page.</p>
<p>The background-image is fixed. Try to scroll down the page.</p>
<p>The background-image is fixed. Try to scroll down the page.</p>
<p>The background-image is fixed. Try to scroll down the page.</p>
<p>The background-image is fixed. Try to scroll down the page.</p>
<p>The background-image is fixed. Try to scroll down the page.</p>
<p>The background-image is fixed. Try to scroll down the page.</p>
<p>The background-image is fixed. Try to scroll down the page.</p>
<p>The background-image is fixed. Try to scroll down the page.</p>
<p>The background-image is fixed. Try to scroll down the page.</p>
<p>The background-image is fixed. Try to scroll down the page.</p>
<p>The background-image is fixed. Try to scroll down the page.</p>
<p>The background-image is fixed. Try to scroll down the page.</p>
<p>The background-image is fixed. Try to scroll down the page.</p>
<p>The background-image is fixed. Try to scroll down the page.</p>
<p>The background-image is fixed. Try to scroll down the page.</p>
</body>
</html>
Result:
Example
Specify that the background image should scroll with the rest of the page:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
body {
background-image: url("img_tree.png");
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-position: right top;
margin-right: 200px;
background-attachment: scroll;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>The background-attachment Property</h1>
<p>The background-attachment property specifies whether the background image should scroll or be fixed (will not scroll with the rest of the page).</p>
<p><strong>Tip:</strong> If you do not see any scrollbars, try to resize the browser window.</p>
<p>The background-image scrolls. Try to scroll down the page.</p>
<p>The background-image scrolls. Try to scroll down the page.</p>
<p>The background-image scrolls. Try to scroll down the page.</p>
<p>The background-image scrolls. Try to scroll down the page.</p>
<p>The background-image scrolls. Try to scroll down the page.</p>
<p>The background-image scrolls. Try to scroll down the page.</p>
<p>The background-image scrolls. Try to scroll down the page.</p>
<p>The background-image scrolls. Try to scroll down the page.</p>
<p>The background-image scrolls. Try to scroll down the page.</p>
<p>The background-image scrolls. Try to scroll down the page.</p>
<p>The background-image scrolls. Try to scroll down the page.</p>
<p>The background-image scrolls. Try to scroll down the page.</p>
<p>The background-image scrolls. Try to scroll down the page.</p>
<p>The background-image scrolls. Try to scroll down the page.</p>
<p>The background-image scrolls. Try to scroll down the page.</p>
<p>The background-image scrolls. Try to scroll down the page.</p>
<p>The background-image scrolls. Try to scroll down the page.</p>
<p>The background-image scrolls. Try to scroll down the page.</p>
<p>The background-image scrolls. Try to scroll down the page.</p>
<p>The background-image scrolls. Try to scroll down the page.</p>
<p>The background-image scrolls. Try to scroll down the page.</p>
</body>
</html>
Result:

CSS background – Shorthand property
To shorten the code, it is also possible to specify all the background properties in one single property. This is called a shorthand property.
Instead of writing:body {
background-color: #ffffff;
background-image: url(“img_tree.png”);
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-position: right top;
}
You can use the shorthand property background:
Example
Use the shorthand property to set the background properties in one declaration:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
body {
background: #ffffff url("img_tree.png") no-repeat right top;
margin-right: 200px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>The background Property</h1>
<p>The background property is a shorthand property for specifying all the background properties in one declaration.</p>
<p>Here, the background image is only shown once, and it is also positioned in the top-right corner.</p>
<p>We have also added a right margin, so that the text will not write over the background image.</p>
</body>
</html>
Result:

When using the shorthand property the order of the property values is:
background-colorbackground-imagebackground-repeatbackground-attachmentbackground-position
It does not matter if one of the property values is missing, as long as the other ones are in this order. Note that we do not use the background-attachment property in the examples above, as it does not have a value.
