Introduction to accounting principles
Accounting is an integral part of every business regardless of business size. With modern-day business requirements, business and accounting are simply inseparable. By recording all the financial transactions, accounting helps in determining the financial performance of the business by preparing financial statements. These financial statements are used by both internal stakeholders as well as external like investors, tax authorities, regulators, banks, etc.
Now imagine, if each business prepares the financial statement in their own way, we all will have hundreds of thousands of financial statements formats trying to convey the same information. This becomes practically impossible for a business compare and read the other companies’ statements. As a result, financial data becomes unusable. Here is why Accounting principles helps to bridge the gap and aims to bring some level of uniformity in financial reporting.
Meaning and definition of accounting principle
Accounting principle refers to common rules or guidelines for accounting financial transactions and preparing financial statements. Accounting principles are the foundational guidelines for recording and preparing financial statements. The accounting principles are commonly referred to as ‘Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP).
Accounting principles help to bring uniformity in accounting and preparing financial statements and it is followed worldwide. The regulators and authorities of each country may have their own accounting principles like UK GAAP, USA GAAP, IFRS etc. but at the core, the fundamentals and objective of accounting principles remain the same.
Conditions of accounting principles
Accounting principles, as a body of doctrines commonly associated with the theory and procedures of accounting, justify the current practice and financial reporting. You or your accountant may choose a method to account and prepare the financial statement while another accountant chooses a different method. Both can be said to be correct only if the accounting principles applied are acceptable and to be acceptable, it should satisfy the following conditions:
- Accounting principles should be based on realistic assumptions.
- Accounting principles must be simple, understandable and explanatory.
- Accounting principles should be followed consistently
- Accounting principles should be able to reflect future predictions
- Accounting principles should be informative for the users.
Accounting principles spectrum – A diagrammatic representation
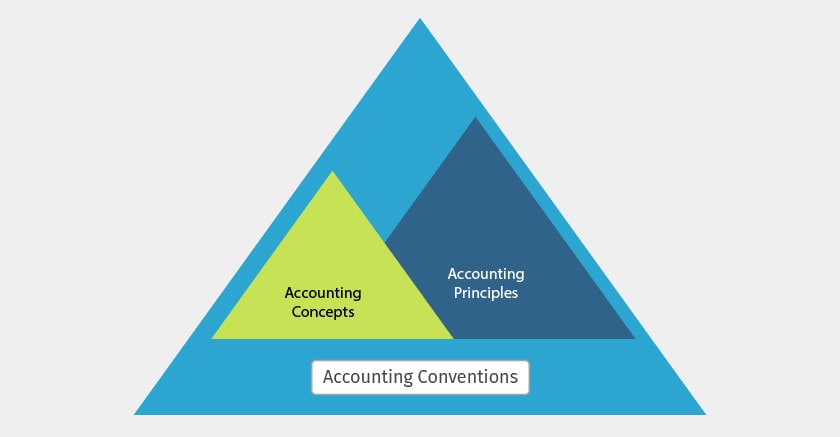
Types of accounting principles
Accounting Principles involves accounting concepts and accounting conventions. For you to understand the accounting principles, you need to know these accounting concepts and conventions.
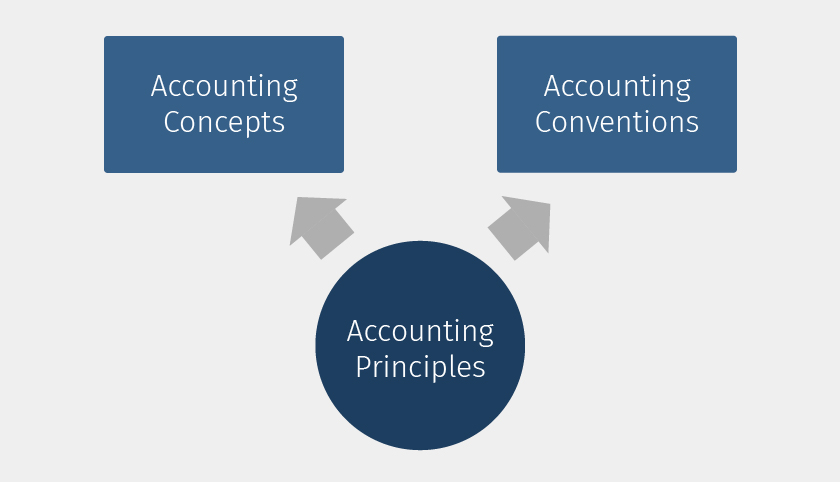
Let us first understand the accounting concepts as a first step to get the accounting principles right. Among the several accounting concepts, the following are some of the important.
- Money measurement principle: In accounting, all the business transactions are measured in terms of money as a common unit of measurement. Since money is the common unit of measurement, as an accounting principle, you are allowed to record only those transactions or events which can be measured or expressed in terms of money.
- Business entity concept: This concept of accounting principle views business and business owner separately as far as their financial transactions are concerned. Legally, your business can exist independently of you and your firm can sue or can be sued in its own name.
- Going-concern principle: This principle applies that all the transactions are recorded on the assumption that the business will remain in operation for a long time and will be able to carry out its obligations as per the plan.
- Cost principle: This accounting principle sets the rules for accounting the fixed assets. According to the cost principle, all the fixed assets are accounted at the original price i.e. the price paid to procure it and subsequently, every year, value is depreciated based on usage, wear and tear, accidents, the passage of time etc.
- Dual-aspect concept: This accounting principle states that for every debit, corresponding credit is made. This is the foundation on which the accounting system is carried out. This is important for you to understand in detail. Read our article ‘Accounting – The Language of Business’ to know more about it.
- Accounting year concept: This implies that each business chooses a specific time period to complete the accounting cycle and financial reporting. In short, this principle talks about the periodicity of accounting. The period can be monthly, quarterly or annually.
- Matching concept: The concept stress on the Accounting principle that if any revenue is recognized then expenses related to earn that revenue should also be recognized. This gives a true picture of profit earned during the accounting period.
- Realization concept: The accounting concept implies that revenue is reported when it’s earned, regardless of when payment is received. Anything paid or received is not considered as profit until the goods or services have been delivered to the buyer
Accounting conventions
After accounting concepts, the next important part of accounting principles is accounting conventions. Accounting conventions refers to a set of customs and traditions that guide the business in preparing the accounting statement. These conventions are derived by usage and practice. The following are the 4 accounting conventions:
- Consistency: consistency is a fundamental assumption that states accounting practices and policies are consistent from one period to another.
- Full disclosure: This convention as part of accounting principles implies that the accounts should be prepared in a manner that all material information is clearly disclosed.
- Conservatism: This convention takes into consideration all prospective losses and leaves all prospective profit until they are earned.
- Materiality: In the materiality principle, all the items having a significant economic effect on the business should be disclosed in the financial statement. All unimportant items are either ignored or merged with other items.
Conclusion
In the end, the aim of accounting is to keep systematic records to ascertain financial performance and financial position of an entity and to communicate the relevant financial information to the interested user groups.
The accounting financial statements are basic means through which the management of an entity makes public communication of the financial information along with selected quantitative details. And such quantitative details could well be maintained with help of ERP Systems such as Tally.ERP 9 following the Accounting Principles laid by statutory organizations.
