Websites often display content in multiple columns (like a magazine or a newspaper).
HTML Layout Elements
HTML has several semantic elements that define the different parts of a web page:
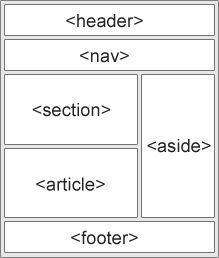
<header>– Defines a header for a document or a section<nav>– Defines a set of navigation links<section>– Defines a section in a document<article>– Defines an independent, self-contained content<aside>– Defines content aside from the content (like a sidebar)<footer>– Defines a footer for a document or a section<details>– Defines additional details that the user can open and close on demand<summary>– Defines a heading for the<details>element
HTML Layout Techniques
There are four different techniques to create multicolumn layouts. Each technique has its pros and cons:
- CSS framework
- CSS float property
- CSS flexbox
- CSS grid
CSS Frameworks
If you want to create your layout fast, you can use a CSS framework, like Bootstrap.
CSS Float Layout
It is common to do entire web layouts using the CSS float property. Float is easy to learn – you just need to remember how the float and clear properties work. Disadvantages: Floating elements are tied to the document flow, which may harm the flexibility. Learn more about float in our CSS Float and Clear chapter.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>CSS Template</title>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<style>
* {
box-sizing: border-box;
}
body {
font-family: Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif;
}
/* Style the header */
header {
background-color: #666;
padding: 30px;
text-align: center;
font-size: 35px;
color: white;
}
/* Create two columns/boxes that floats next to each other */
nav {
float: left;
width: 30%;
height: 300px; /* only for demonstration, should be removed */
background: #ccc;
padding: 20px;
}
/* Style the list inside the menu */
nav ul {
list-style-type: none;
padding: 0;
}
article {
float: left;
padding: 20px;
width: 70%;
background-color: #f1f1f1;
height: 300px; /* only for demonstration, should be removed */
}
/* Clear floats after the columns */
section::after {
content: "";
display: table;
clear: both;
}
/* Style the footer */
footer {
background-color: #777;
padding: 10px;
text-align: center;
color: white;
}
/* Responsive layout - makes the two columns/boxes stack on top of each other instead of next to each other, on small screens */
@media (max-width: 600px) {
nav, article {
width: 100%;
height: auto;
}
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2> CSS Layout Float</h2>
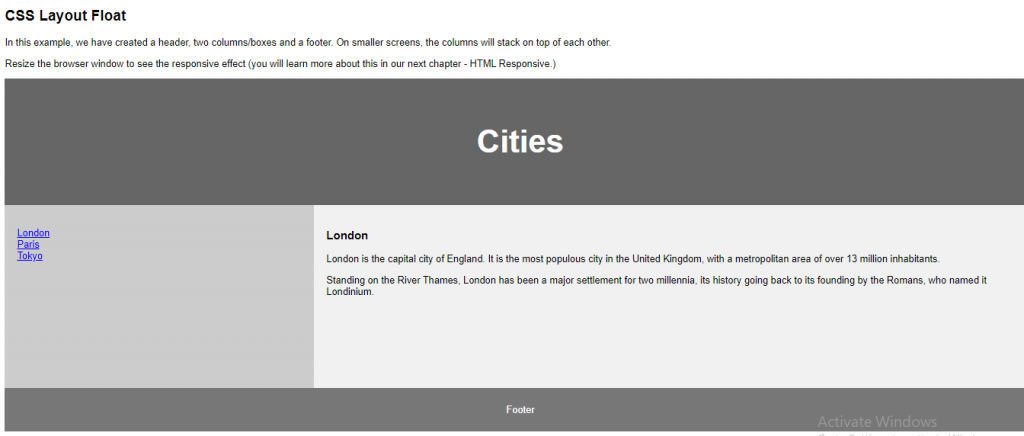
<p>In this example, we have created a header, two columns/boxes and a footer. On smaller screens, the columns will stack on top of each other.</p>
<p>Resize the browser window to see the responsive effect (you will learn more about this in our next chapter - HTML Responsive.)</p>
<header>
<h2>Cities</h2>
</header>
<section>
<nav>
<ul>
<li><a href="#">London</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Paris</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Tokyo</a></li>
</ul>
</nav>
<article>
<h1>London</h1>
<p>London is the capital city of England. It is the most populous city in the United Kingdom, with a metropolitan area of over 13 million inhabitants.</p>
<p>Standing on the River Thames, London has been a major settlement for two millennia, its history going back to its founding by the Romans, who named it Londinium.</p>
</article>
</section>
<footer>
<p>Footer</p>
</footer>
</body>
</html>
CSS Flexbox Layout
Use of flexbox ensures that elements behave predictably when the page layout must accommodate different screen sizes and different display devices.
Learn more about flexbox in our CSS Flexbox chapter.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>CSS Template</title>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<style>
* {
box-sizing: border-box;
}
body {
font-family: Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif;
}
/* Style the header */
header {
background-color: #666;
padding: 30px;
text-align: center;
font-size: 35px;
color: white;
}
/* Container for flexboxes */
section {
display: -webkit-flex;
display: flex;
}
/* Style the navigation menu */
nav {
-webkit-flex: 1;
-ms-flex: 1;
flex: 1;
background: #ccc;
padding: 20px;
}
/* Style the list inside the menu */
nav ul {
list-style-type: none;
padding: 0;
}
/* Style the content */
article {
-webkit-flex: 3;
-ms-flex: 3;
flex: 3;
background-color: #f1f1f1;
padding: 10px;
}
/* Style the footer */
footer {
background-color: #777;
padding: 10px;
text-align: center;
color: white;
}
/* Responsive layout - makes the menu and the content (inside the section) sit on top of each other instead of next to each other */
@media (max-width: 600px) {
section {
-webkit-flex-direction: column;
flex-direction: column;
}
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>CSS Layout Flexbox</h2>
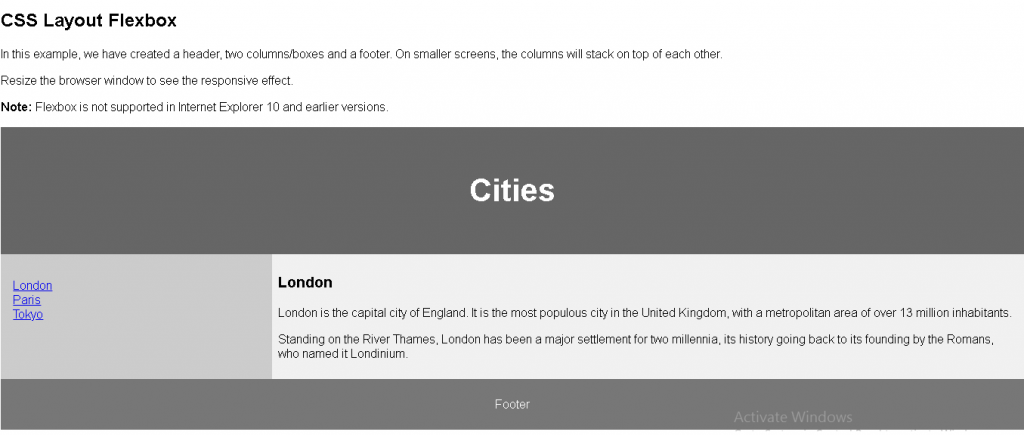
<p>In this example, we have created a header, two columns/boxes and a footer. On smaller screens, the columns will stack on top of each other.</p>
<p>Resize the browser window to see the responsive effect.</p>
<p><strong>Note:</strong> Flexbox is not supported in Internet Explorer 10 and earlier versions.</p>
<header>
<h2>Cities</h2>
</header>
<section>
<nav>
<ul>
<li><a href="#">London</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Paris</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Tokyo</a></li>
</ul>
</nav>
<article>
<h1>London</h1>
<p>London is the capital city of England. It is the most populous city in the United Kingdom, with a metropolitan area of over 13 million inhabitants.</p>
<p>Standing on the River Thames, London has been a major settlement for two millennia, its history going back to its founding by the Romans, who named it Londinium.</p>
</article>
</section>
<footer>
<p>Footer</p>
</footer>
</body>
</html>
CSS Grid Layout
The CSS Grid Layout Module offers a grid-based layout system, with rows and columns, making it easier to design web pages without having to use floats and positioning.
Learn more about CSS grids in our CSS Grid Intro chapter.
