The HTML class attribute is used to specify a class for an HTML element.
Multiple HTML elements can share the same class.
Using The class Attribute
The class attribute is often used to point to a class name in a style sheet. It can also be used by a JavaScript to access and manipulate elements with the specific class name.
In the following example we have three <div> elements with a class attribute with the value of “city”. All of the three <div> elements will be styled equally according to the .city style definition in the head section:
Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
.city {
background-color: tomato;
color: white;
border: 2px solid black;
margin: 20px;
padding: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class=”city”>
<h2>London</h2>
<p>London is the capital of England.</p>
</div>
<div class=”city”>
<h2>Paris</h2>
<p>Paris is the capital of France.</p>
</div>
<div class=”city”>
<h2>Tokyo</h2>
<p>Tokyo is the capital of Japan.</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>

In the following example we have two <span> elements with a class attribute with the value of “note”. Both <span> elements will be styled equally according to the .note style definition in the head section:
Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
.note {
font-size: 120%;
color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
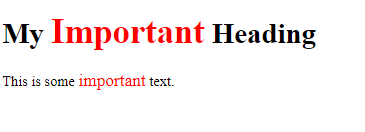
<h1>My <span class=”note”>Important</span> Heading</h1>
<p>This is some <span class=”note”>important</span> text.</p>
</body>
</html>
The Syntax For Class
To create a class; write a period (.) character, followed by a class name. Then, define the CSS properties within curly braces {}:
Example
Create a class named “city”:<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
.city {
background-color: tomato;
color: white;
padding: 10px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2 class=”city”>London</h2>
<p>London is the capital of England.</p>
<h2 class=”city”>Paris</h2>
<p>Paris is the capital of France.</p>
<h2 class=”city”>Tokyo</h2>
<p>Tokyo is the capital of Japan.</p>
</body>
</html>

Multiple Classes
HTML elements can belong to more than one class.
To define multiple classes, separate the class names with a space, e.g. <div class=”city main”>. The element will be styled according to all the classes specified.
In the following example, the first <h2> element belongs to both the city class and also to the main class, and will get the CSS styles from both of the classes:
Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
.city {
background-color: tomato;
color: white;
padding: 10px;
}
.main {
text-align: center;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
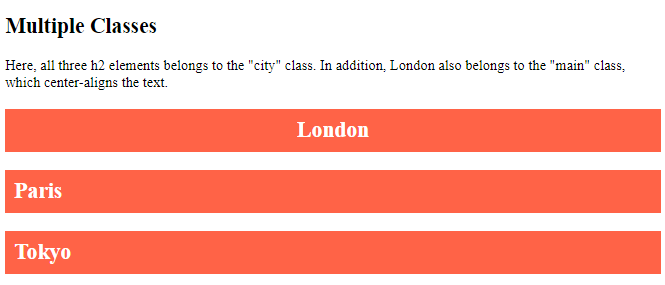
<h2>Multiple Classes</h2>
<p>Here, all three h2 elements belongs to the "city" class. In addition, London also belongs to the "main" class, which center-aligns the text.</p>
<h2 class="city main">London</h2>
<h2 class="city">Paris</h2>
<h2 class="city">Tokyo</h2>
</body>
</html>
Different Elements Can Share Same Class
Different HTML elements can point to the same class name.
In the following example, both <h2> and <p> points to the “city” class and will share the same style:
Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
.city {
background-color: tomato;
color: white;
padding: 10px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Different Elements Can Share Same Class</h2>
<p>Even if the two elements do not have the same tag name, they can both point to the same class, and get the same CSS styling:</p>
<h2 class="city">Paris</h2>
<p class="city">Paris is the capital of France.</p>
</body>
</html>

Use of The class Attribute in JavaScript
The class name can also be used by JavaScript to perform certain tasks for specific elements.
JavaScript can access elements with a specific class name with the getElementsByClassName() method:
Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h2>Use of The class Attribute in JavaScript</h2>
<p>Click the button to hide all elements with class name "city":</p>
<button onclick="myFunction()">Hide elements</button>
<h2 class="city">London</h2>
<p>London is the capital of England.</p>
<h2 class="city">Paris</h2>
<p>Paris is the capital of France.</p>
<h2 class="city">Tokyo</h2>
<p>Tokyo is the capital of Japan.</p>
<script>
function myFunction() {
var x = document.getElementsByClassName("city");
for (var i = 0; i < x.length; i++) {
x[i].style.display = "none";
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>


