C supports nesting of loops in C. Nesting of loops is the feature in C that allows the looping of statements inside another loop.
Syntax of Nested loop
- Outer_loop
- {
- Inner_loop
- {
- // inner loop statements.
- }
- // outer loop statements.
- }
Outer_loop and Inner_loop are the valid loops that can be a ‘for’ loop, ‘while’ loop or ‘do-while’ loop.
Nested for loop
The nested for loop means any type of loop which is defined inside the ‘for’ loop.
- for (initialization; condition; update)
- {
- for(initialization; condition; update)
- {
- // inner loop statements.
- }
- // outer loop statements.
- }
Example of nested for loop
- #include <stdio.h>
- int main()
- {
- int n;// variable declaration
- printf(“Enter the value of n :”);
- // Displaying the n tables.
- for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) // outer loop
- {
- for(int j=1;j<=10;j++) // inner loop
- {
- printf(“%d\t”,(i*j)); // printing the value.
- }
- printf(“\n”);
- }
Explanation of the above code
- First, the ‘i’ variable is initialized to 1 and then program control passes to the i<=n.
- The program control checks whether the condition ‘i<=n’ is true or not.
- If the condition is true, then the program control passes to the inner loop.
- The inner loop will get executed until the condition is true.
- After the execution of the inner loop, the control moves back to the update of the outer loop, i.e., i++.
- After incrementing the value of the loop counter, the condition is checked again, i.e., i<=n.
- If the condition is true, then the inner loop will be executed again.
- This process will continue until the condition of the outer loop is true.
Output:
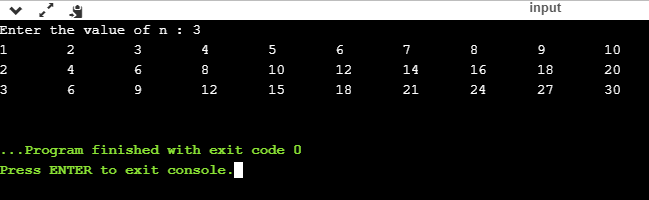
Nested while loop
The nested while loop means any type of loop which is defined inside the ‘while’ loop.
- while(condition)
- {
- while(condition)
- {
- // inner loop statements.
- }
- // outer loop statements.
- }
Example of nested while loop
- #include <stdio.h>
- int main()
- {
- int rows; // variable declaration
- int columns; // variable declaration
- int k=1; // variable initialization
- printf(“Enter the number of rows :”); // input the number of rows.
- scanf(“%d”,&rows);
- printf(“\nEnter the number of columns :”); // input the number of columns.
- scanf(“%d”,&columns);
- int i=1;
- while(i<=rows) // outer loop
- {
- int j=1;
- while(j<=columns) // inner loop
- {
- printf(“%d\t”,k); // printing the value of k.
- k++; // increment counter
- j++;
- }
- i++;
- printf(“\n”);
- }
- }
Explanation of the above code.
- We have created the 2d array, i.e., int a[rows][columns].
- The program initializes the ‘i’ variable by 1.
- Now, control moves to the while loop, and this loop checks whether the condition is true, then the program control moves to the inner loop.
- After the execution of the inner loop, the control moves to the update of the outer loop, i.e., i++.
- After incrementing the value of ‘i’, the condition (i<=rows) is checked.
- If the condition is true, the control then again moves to the inner loop.
- This process continues until the condition of the outer loop is true.
Output:
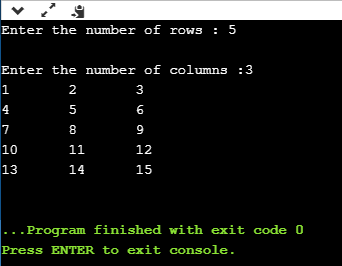
Nested do..while loop
The nested do..while loop means any type of loop which is defined inside the ‘do..while’ loop.
- do
- {
- do
- {
- // inner loop statements.
- }while(condition);
- // outer loop statements.
- }while(condition);
Example of nested do..while loop.
- #include <stdio.h>
- int main()
- {
- /*printing the pattern
- ********
- ********
- ********
- ******** */
- int i=1;
- do // outer loop
- {
- int j=1;
- do // inner loop
- {
- printf(“*”);
- j++;
- }while(j<=8);
- printf(“\n”);
- i++;
- }while(i<=4);
- }
Output:
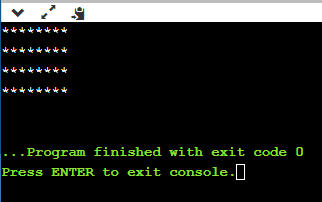
Explanation of the above code.
- First, we initialize the outer loop counter variable, i.e., ‘i’ by 1.
- As we know that the do..while loop executes once without checking the condition, so the inner loop is executed without checking the condition in the outer loop.
- After the execution of the inner loop, the control moves to the update of the i++.
- When the loop counter value is incremented, the condition is checked. If the condition in the outer loop is true, then the inner loop is executed.
- This process will continue until the condition in the outer loop is true.
